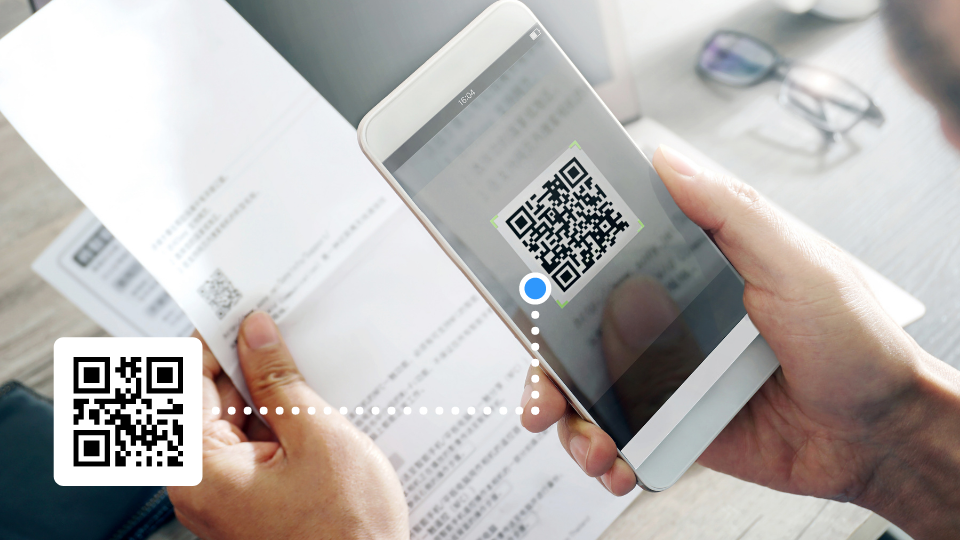
A Treasury bank includes QR codes and barcode in accountholder reports. Accountholders scan the codes to access detailed financial analyses, portfolio updates, within its secure transaction portals, simplifying data bank management.
QR codes link additional details on a particular offer or scheme, provide details on social initiatives, and allow customers to download a particular mobile application to manage their bank account or credit card, among others. QR codes can also be used for accountholders non-financial applications within the payment’s application. For example, they can be used to link to Treasury Bank’s portals and to assert their identity and authentication.
Tokenization
Tokenization enables a diverse set of Treasury Bank secured credit transfer to and from members accounts via secure tokens via rest API, for Remote Deposit Capture RDC or Remote Cash Capture RCC via wholesale lockbox, Image or cash letter with API mapping, barcore stipe or QRC print with Magnetic Ink Character Reconition MICR.
Asset Management

QR Code is also an Asset management tool that ensure that accountholders stay on top of all tracking-related investment processes their physical assets and inventory.
With a robust and clearly-outlined asset tracking framework in place, accountholders can save on time, trim costs, improve efficiency, do quick asset audits, and have all your asset data within your fingertips.
With QR Codes, treasury and bank personnel can simply use their smartphones and scan the asset to either view asset and payment info or log data into the central asset tracking database. Again, all it takes is a single scan—without any dedicated scanning equipment or setup required.
QR Code equity and financial data tracking can be set up easily and integrated with all the software tools that all parties already use for business through API. Treasury Bank is a use third-party integration platforms Integromat to link the codes with treasury software using API.
A smartphone’s built-in QR Code reader acts as the interface between your product and the information stored on Treasury Bank asset management system.
Therefore, QR Codes for asset management allow accountholders to instantly view and edit data about equity investment.
Additionally, QR Codes tokenize data, to provide businesses with enhanced security and transparency in tracking their physical assets, making the management process even more efficiency and accountability and make it easy to create a fixed asset register automatically.
A fixed asset register is nothing but a detailed roster of all the physical assets and program development owned and used by a accountholder such as manufacturing equipment or even office hardware like laptops, printers, chairs, and desks.
QR Codes for asset management can help businesses monitor their fixed assets closely by tracking their location and who they are handled by. In addition, they also help with the transparency of the condition and status of these assets.
International Payment
The Treasury Bank utilizes QR Codes and Bar Code with the Fast Payment Systems (FPS) of Project FASTT that is used by central banks and private players across the globe. FPS policy toolkit is toolkit is a payment guide in many countries and regions. Project FPS Toolkit was supported by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation. The toolkit can be found at fastpayments.worldbank.org and consists of the following components
As fast payment systems (FPS) evolve, they enable a diverse set of payment service providers (banks and non-banks) and support a variety of payment instruments, use cases (domestic and cross-border), transaction channels, and overlay services. The Payment Systems Development Group (PSDG) of the World Bank has assisted more than 120 countries in modernizing their payment systems over the years and, more recently, has played a leading role in global research and technical assistance to countries on fast payments. Project FASTT, is a new milestone in this critical work, supported by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation through the Finance for Development (F4D) Umbrella Program.
This note is part of the third component of the toolkit and aims to provide inputs on quick-response (QR) codes from a payment’s perspective, with a focus on fast payments.
Treasury Bank enforces mobile penetration with an initial push for QR code for it payment services and a way to exchange the information required to initiate and/or receive payments. QR codes are used to convey the account details of accountholders to convey their payment account details to their deposit bank accounts. Once the information is captured, a credit transfer to the Accountholder bank is initiated. In the latter case, a request to pay (RTP) is initiated by the payee
Accountholders without bank accounts/cards can also leverage the QR code as a means of making transactions through other payment instruments such as digital securities.
Push and Pull payments deposits,
QR codes can serve as the initiation mechanism for both push and pull payments, including at physical merchants, in wholesale lockbox transactions, for bill payments, and during business-to-business transfers
KYC compliance
Know-your-customer KYC compliance, document collection, verification, and updates applies with the QR code-based acceptance for incorporated association entities, such as payment intermediaries and correspondence banks
Security
Security aspects related to QR codes, including fraud committed by replicating the QR code, identity impersonation, and data protection, are carefully assessed. Investments in back-end security are necessary to ensure secure data transmission and storage. There is a adequate focus on monitoring and enhancing security at the physical, network, and application infrastructure levels.
• Payment applications provide users with a deeper understanding of security. The accountholders name and masked credentials can be displayed after scanning a QR code, to enable safe transactions.
• Details of a payment transaction are displayed for validation before a payment is processed. The service is complemented by real-time notifications to both the payer and the payee.
• Steps are taken to verify the identity of the payee, particularly when the QR codes are used in an RTP framework.
• Third-party entities can conduct the security test and security audit of the application being used for QR code– based payments.
EMVCo
• EMVCo believes that the security principles for QR codes should be similar to those for any software-based mobile-payment mechanism. The typical layered approach should be with data-at-rest security, data-under-processing security, and data-transmission security.
To drive security and reduce fraud, similar to what happens with a contactless transaction, the EMV16 QR code specification does not transmit any confidential information
Additionally, Ant Group has been working with experts from different markets in ISO/TC68 Financial Services/SC2 Security/WG19 Security on aspects of code-scanning payment, to establish the new ISO 5201, an international standard on financial services for code-scanning payment security.
The standard17 covers security issues related to code-scanning technologies used for payments and includes an overview, a risk assessment, and minimum security requirements and extended security guidelines for code-scanning payment, where the payer uses a device to operate the payment transaction. The standard is applicable to cases where the code is both used to initiate a payment transaction and presented by the payer or the payee.